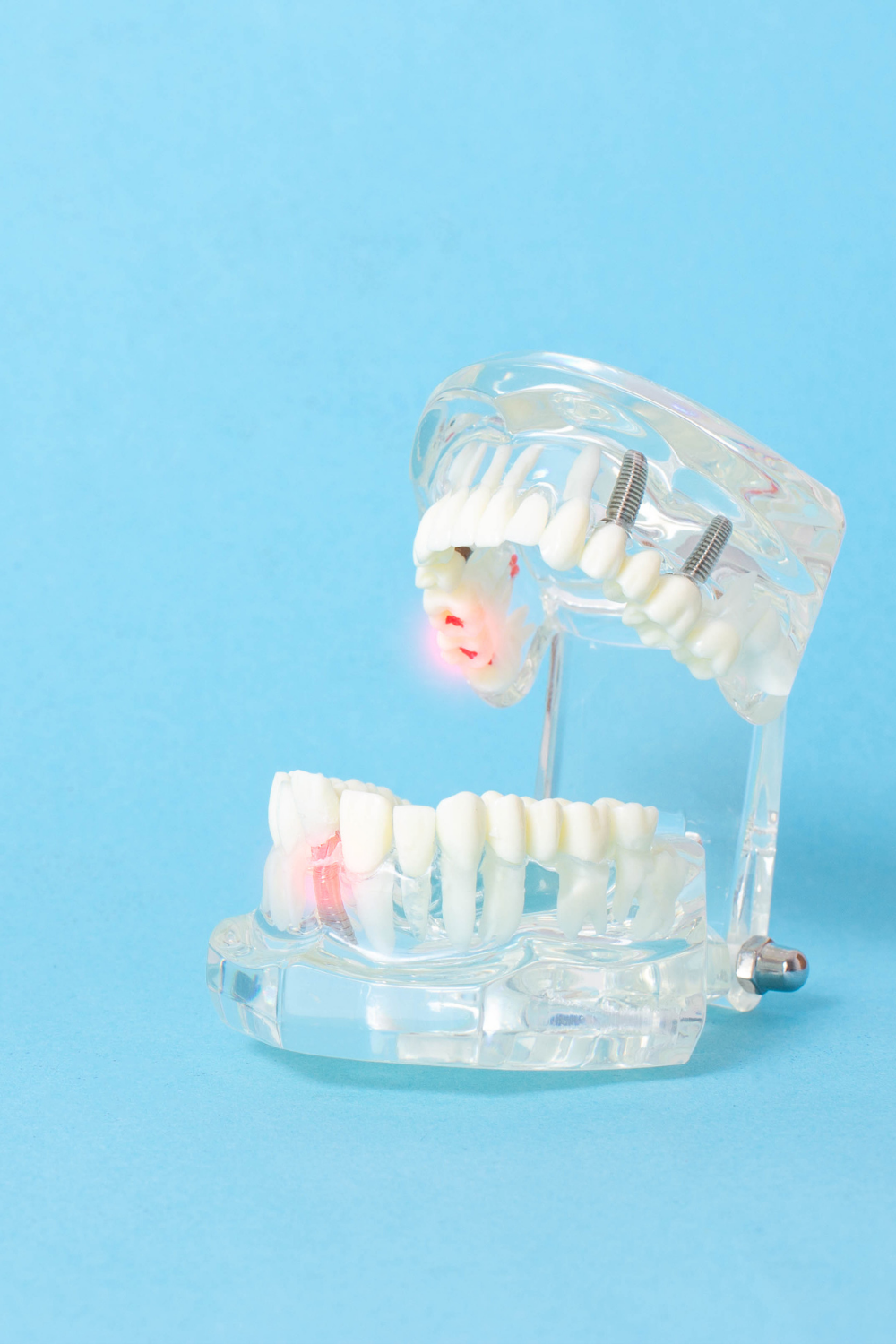
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is an infection that affects the tissues that hold your teeth in position. In most cases, it results from poor flossing and brushing habits resulting in plaque buildup on the teeth, which hardens after time. If left untreated, periodontal disease can damage the bone that supports your teeth, causing the teeth to loosen. It can potentially lead to tooth loss. Since it mainly results from poor hygiene, you can easily prevent periodontitis. If you already have periodontitis, you should visit a dentist specializing in gum disease & periodontics in Novi for early treatment to avoid more severe problems.
Symptoms
When in good health, your gums should appear pale pink and firm. They should also fit perfectly around your teeth. Anything other than this could point towards periodontitis. Common symptoms of periodontitis include:
- Puffy or swollen gums.
- Gums that bleed easily.
- Tender gums.
- Bleeding when brushing or flossing.
- Bad breath.
- Loose teeth or teeth falling out.
- Pain when chewing.
- New spaces between your teeth.
- A change in the alignment of your teeth when you bite.
You need to schedule regular checkups with your dentist. If you experience any of the symptoms associated with periodontitis, book an appointment with a dentist immediately. The sooner you seek treatment, the easier it becomes to reverse the damage caused.
Causes
Most patients develop periodontitis due to a thick sticky film comprised of bacteria (plaque). If untreated, plaque evolves into periodontitis by hardening below the gum line to form tartar. It is harder to clean off and has a lot of bacteria. The more it stays on your teeth, the more the damage. It would be best if you got rid of it since flossing and brushing cannot work.
Plaque can also cause gingivitis which is a mild form of gum disease. It is the inflammation and irritation of a portion of your gum tissue surrounding the base of your teeth. Professional treatment and good oral hygiene can reverse gingivitis.
Gum inflammation that lasts long can also cause periodontitis, resulting in pockets between the teeth and gums. Eventually, the pockets fill up with plaque, bacteria, and tartar. If left untreated, they can lose tissue and bone, potentially causing the loss of one or more teeth. Chronic inflammation can also affect your immune system.
Prevention
The most effective way to prevent periodontitis is by adhering to a good oral hygiene program. Brush your teeth at least two times each day and floss at least once a day. Ideally, floss before brushing to remove the loosened food particles and bacteria.
You should also schedule regular visits to your dentist for professional cleaning. You are advised to see a dentist at least twice a year if you have no dental problems. If you have risk factors that increase your susceptibility to periodontitis, you may need to visit a dentist more often.
In summary, periodontal disease is an infection that affects the tissues that hold your teeth in position. Common symptoms of gum disease include puffy or swollen gums, bleeding when brushing or flossing, and tender gums. It primarily results from poor oral hygiene. You can prevent it by following a good oral hygiene program and visiting a dentist regularly.