How common is chronic pain? More common than you think. According to the CDC, approximately 20% of adults live with it in the United States.
What can cause it? A lot of things. For instance, it might be due to arthritis, multiple sclerosis, neuropathy, ulcers, or fibromyalgia.
Fortunately, there are various treatments available for alleviating symptoms. Take painkillers, for example—they’re often prescribed for those with chronic pain.
There are other options as well such as extracorporeal shock wave therapy. What is it? How does it work?
Want to know? If so, be sure to keep reading—because that’s what we’ll be discussing below!
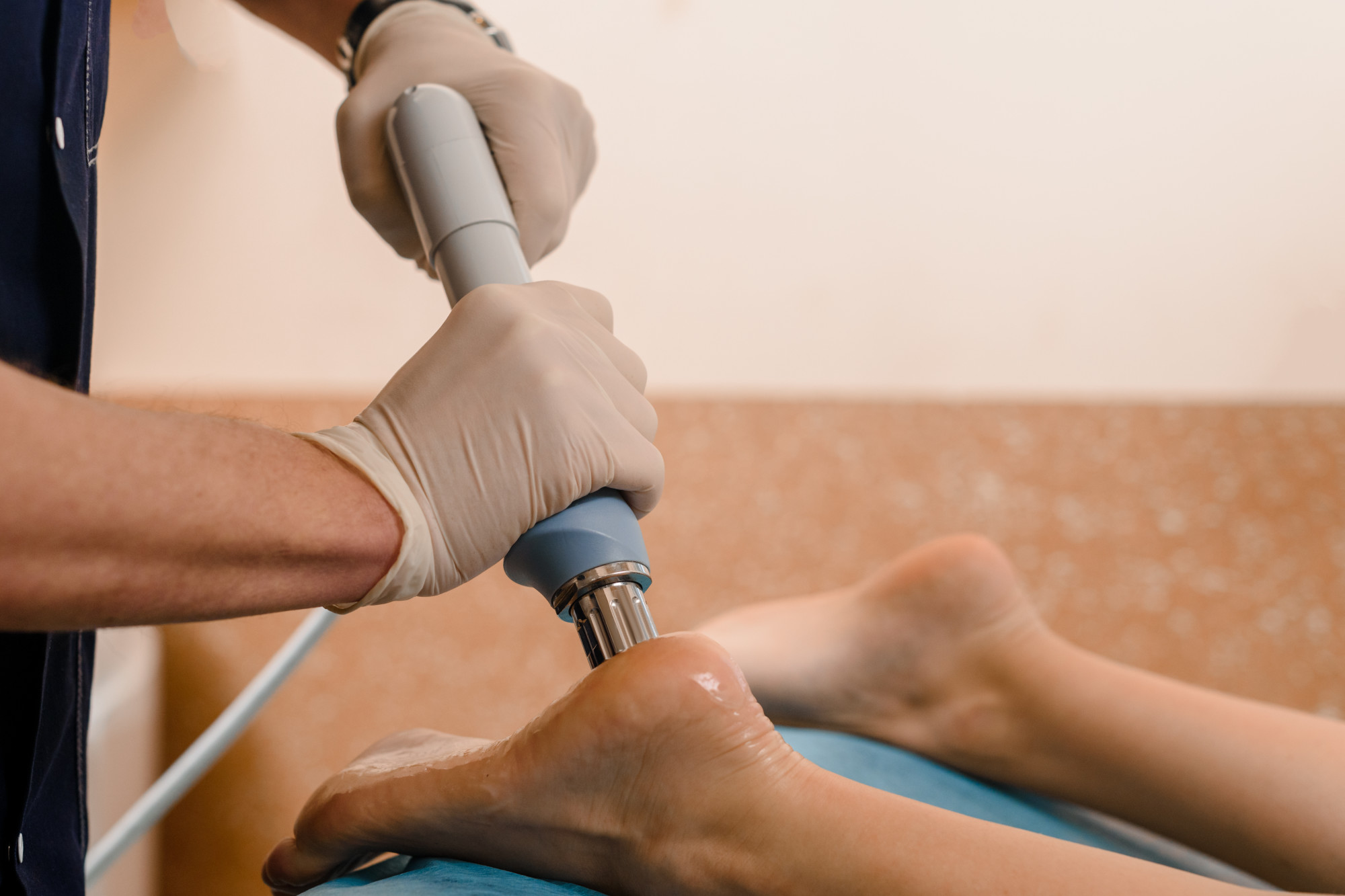
What is Shock Wave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy is a non-invasive treatment that’s used to relieve pain. Used in physiotherapy and orthopedics, it involves the delivery of shock waves (thus its name) to injured tissues.
It’s effective for many musculoskeletal conditions, especially those that involve the connective tissues such as tendons and ligaments. Generally speaking, it’s reserved for those who haven’t responded to other forms of treatment.
How Does Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Work?
Shockwave therapy treats pain with a series of low energy waves. These pulsations are applied directly to the area through the skin.
From there, they interact with the tissue—this causes accelerated tissue repair and cell growth. Put it simply, the waves will trigger the body’s natural healing response.
What Can You Use Shock Wave Therapy For?
Shockwave therapy can be used to treat various ailments such as Achilles tendonitis, bursitis, iliotibial band friction syndrome, and neuroma. In addition to that, it’s also effective for back pain.
Aside from that, studies have shown that it can also be effective for other conditions. For example, some people use shockwave therapy for ED.
Contraindications and Potential Side Effects
Shockwave therapy is generally safe, as long as you don’t have bone diseases, connective tissue disorders, or active cancer.
It should also not be used on open wounds or during pregnancy. Those who’re using blood-thinning medications are also not eligible.
In terms of side effects, most people will experience mild bruising, numbness, pain, tingling, or swelling in the treated area. With that said, these symptoms will typically go away within 1-2 days.
What to Expect
Most people will require a series of treatments, each of which is less than 30 minutes long. The majority of patients will feel better after 6-12 sessions, though the exact number depends on the condition.
As for the therapy itself, it can cause a bit of discomfort. However, it’s bearable for most individuals.
Some therapists are also able to adjust the intensity according to the patient’s tolerance.
Relieving Pain
Hopefully, that gives you a better idea as to how extracorporeal shock wave therapy works. As you can see, it’s effective for a variety of conditions!
Looking for more health-related posts? If so, be sure to check out some of our other blog articles!


